Generation Modes
The Write module provides multiple ways to generate content, from a single article to hundreds at once. These methods are organized into different modes, accessible via tabs.
- Single: Generates one article at a time directly in the interface.
- Bulk, CSV, RSS, URL, Google Sheets: These modes create automated tasks for generating content in the background.
Single
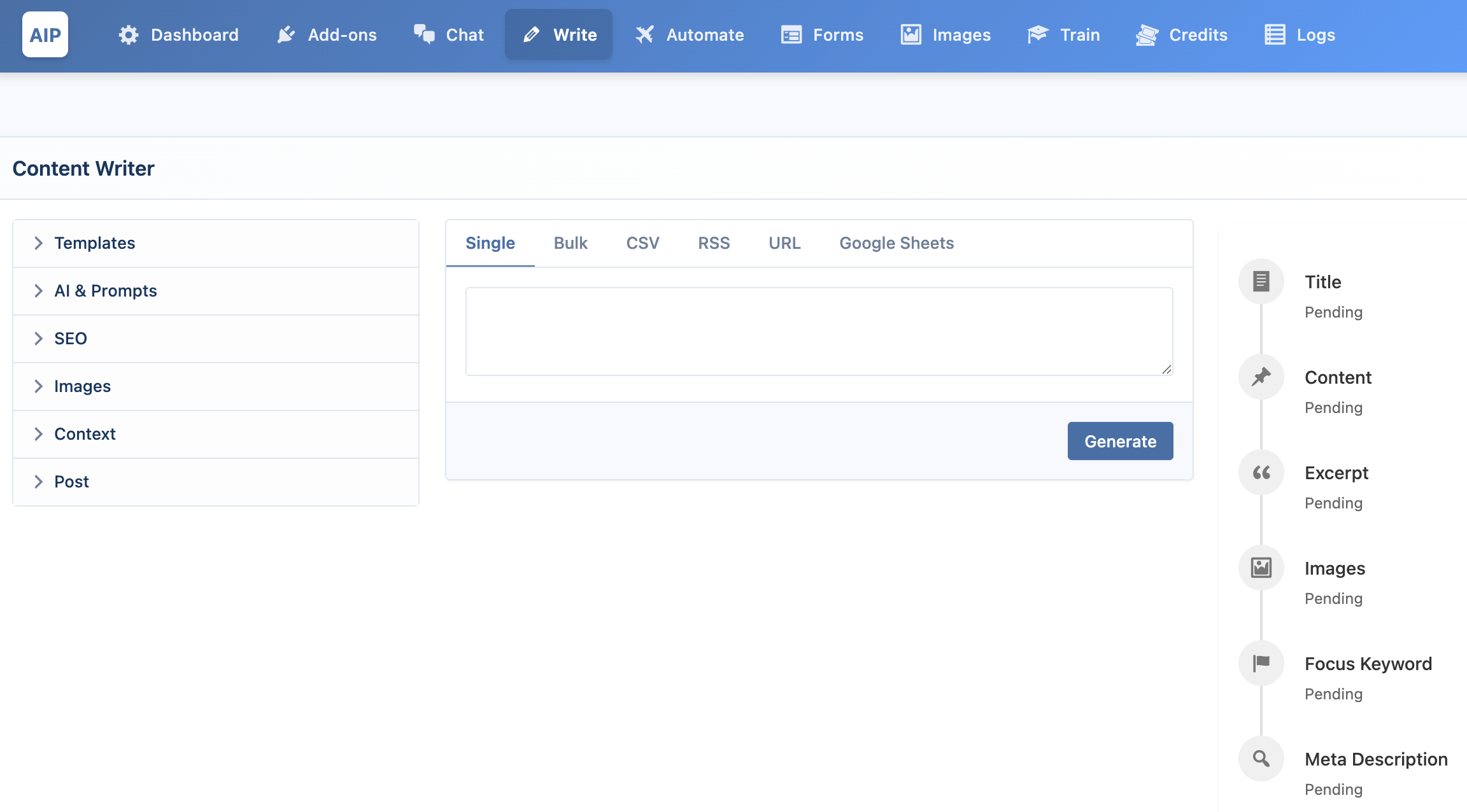
This is the most straightforward way to create content. Simply enter your topic (and optionally, keywords separated by a |) into the text box and click Generate.
The AI will generate a title and the full article, which will appear in the output panel on the right. This allows you to review, copy, or save the content as a post immediately.
Example Input:
How to train a puppy | puppy training, housebreaking, new dog
List
For generating multiple articles, you can use one of the task-based modes. When you use these modes, instead of generating content immediately, AIP creates a task that runs in the background.
Task-based generation is managed by the Automate module. This section provides a brief overview. For detailed information on managing, monitoring, and scheduling, please see the Automate documentation.
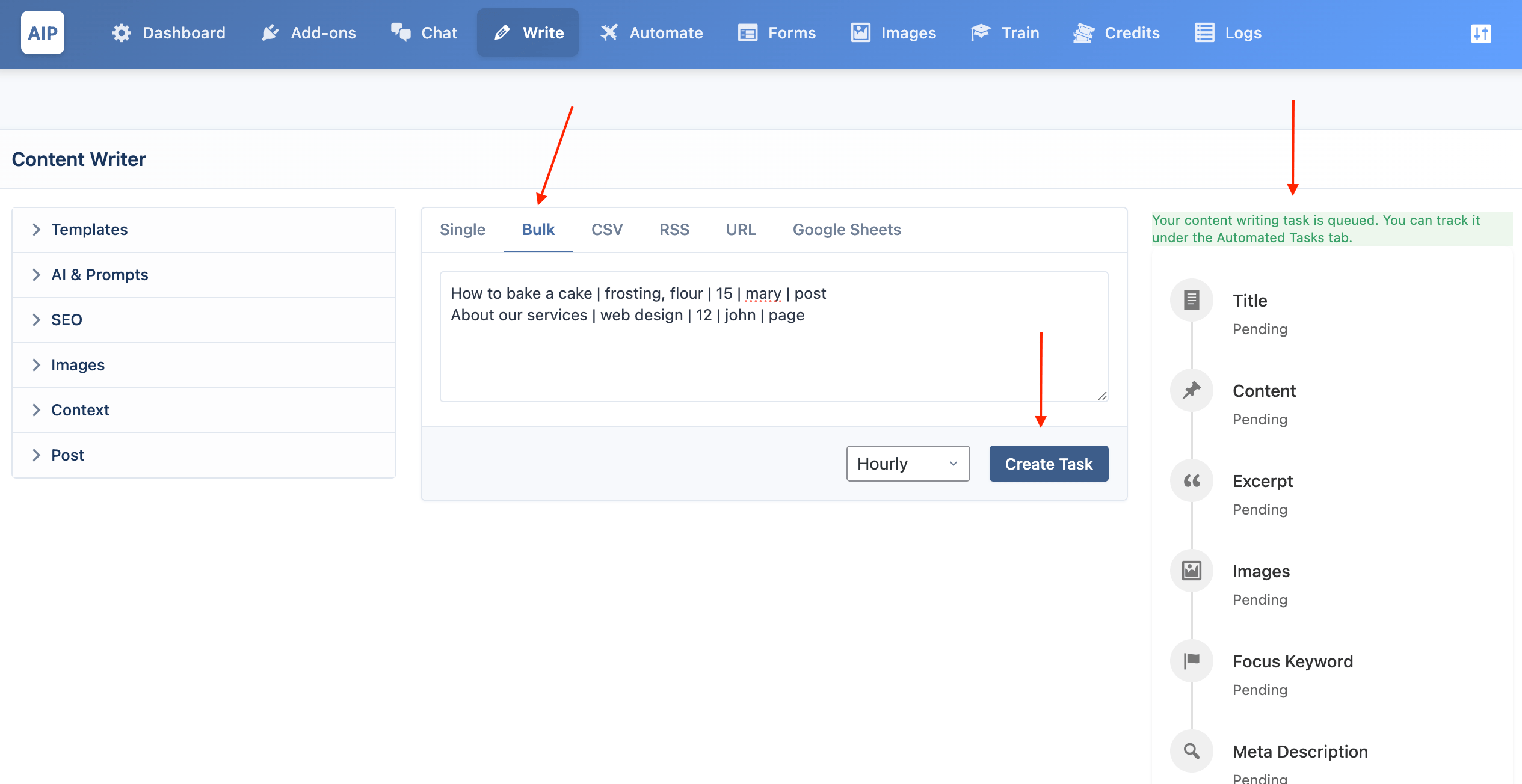
The Bulk mode allows you to enter a list of topics directly.
-
Format: Enter one topic per line. You can also include keywords, a category ID, author username, post type slug, and schedule date separated by
|. -
Example:
How to bake a cake | frosting, flour | 15 | mary | post
About our services | web design | 12 | john | page | 2025-12-25 14:30
The future of AI in marketing
CSV
This mode lets you generate articles by importing topics from a CSV file.
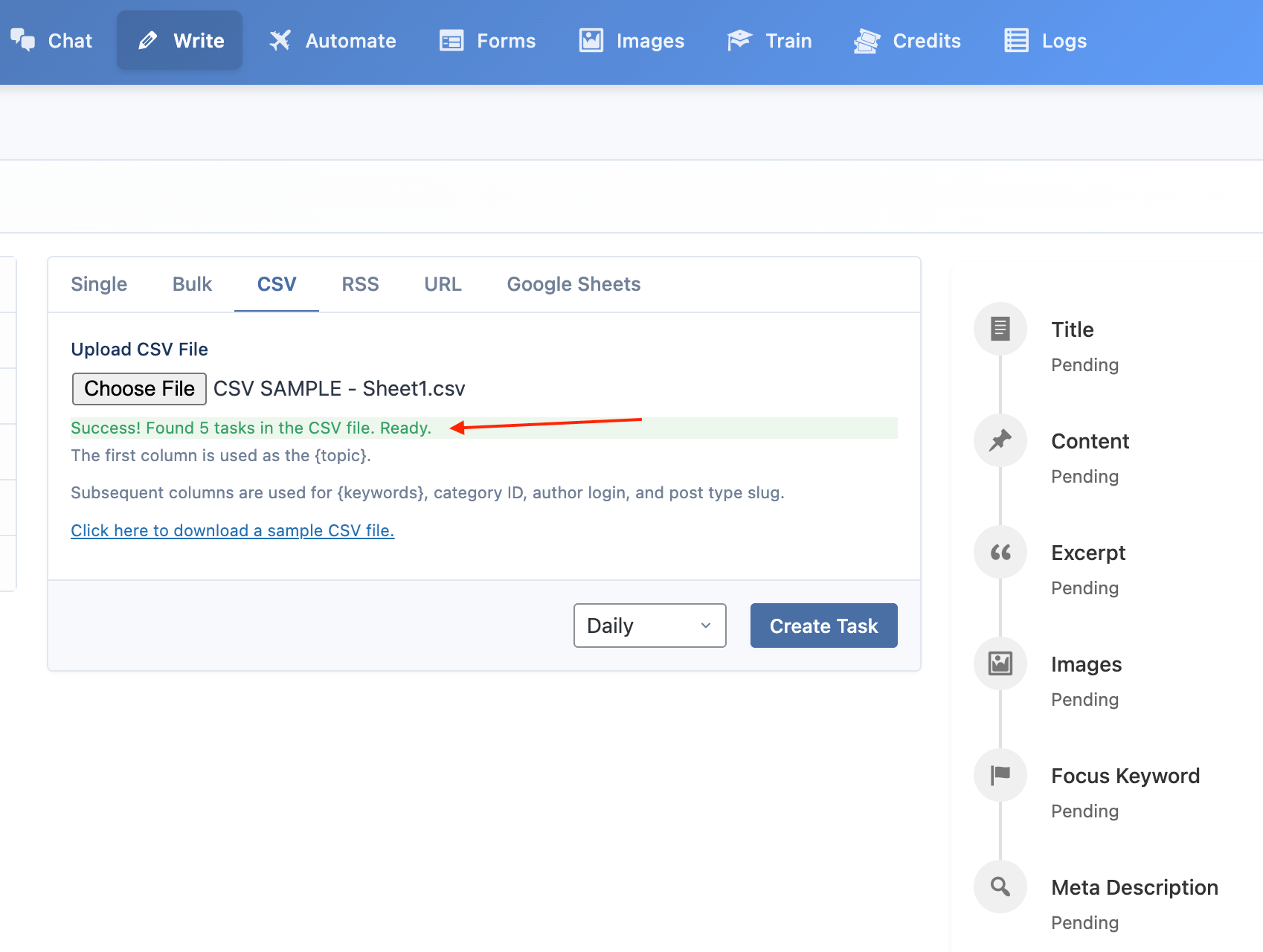
- Format: The columns in your CSV file must be in the following order:
Topic,Keywords,Category ID,Author Username,Post Type Slug,Schedule Date (YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM). - Usage: Click "Choose File" to upload your CSV. The system will parse the file and prepare the topics for the task.
To ensure you have the correct format, you can download a sample CSV file here.
RSS
This mode automatically creates articles from new items in one or more RSS feeds.
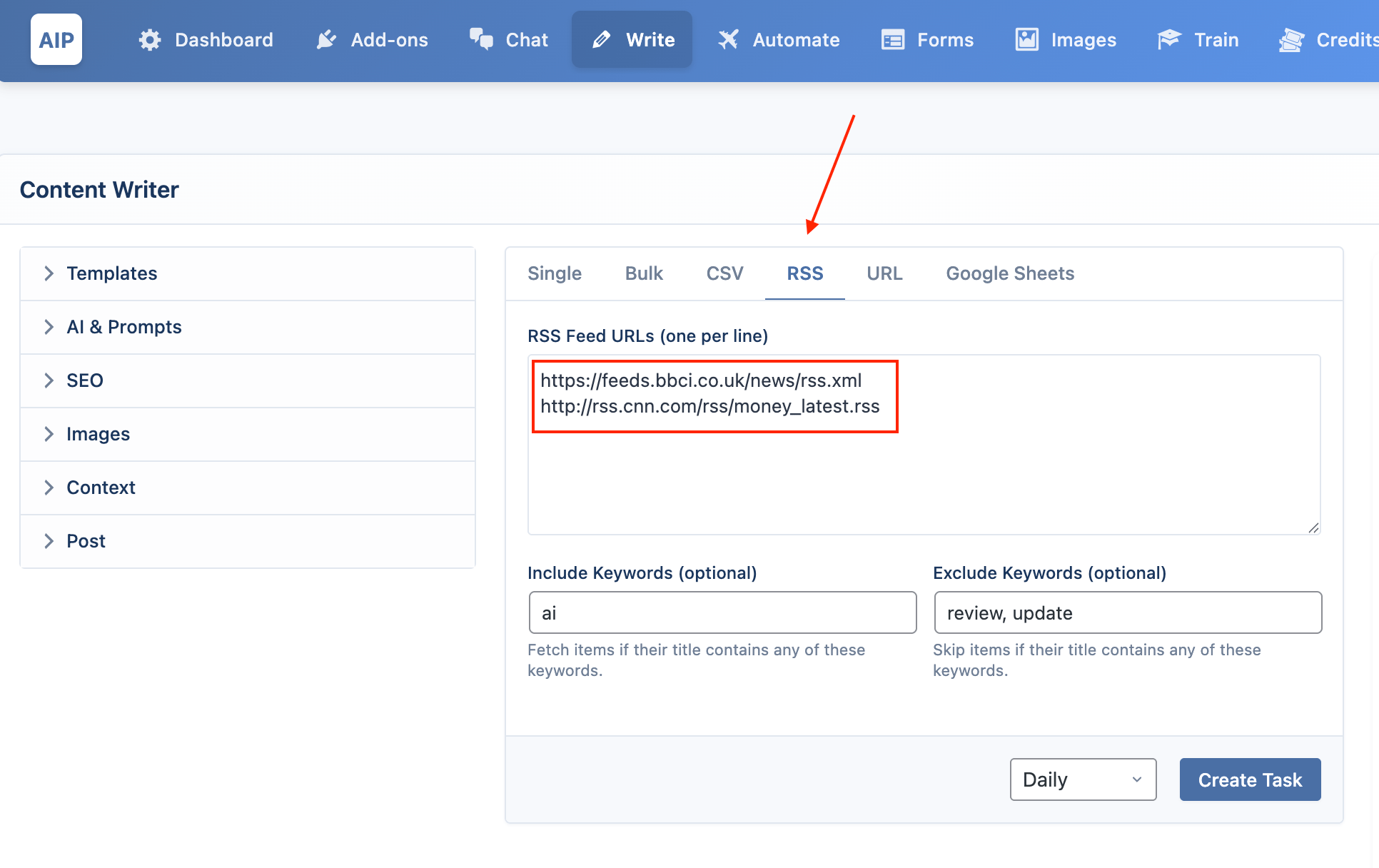
- Format: Enter one RSS feed URL per line in the provided text area.
- Filtering: You can use the Include Keywords and Exclude Keywords fields to control which feed items are used to generate content.
- Prompting: Use the
{description}and{source_url}placeholders in your prompt to include the item's description and URL from the RSS feed as context.
URL
This mode generates articles by fetching content from a list of URLs. This is useful for summarizing or rewriting existing web pages.
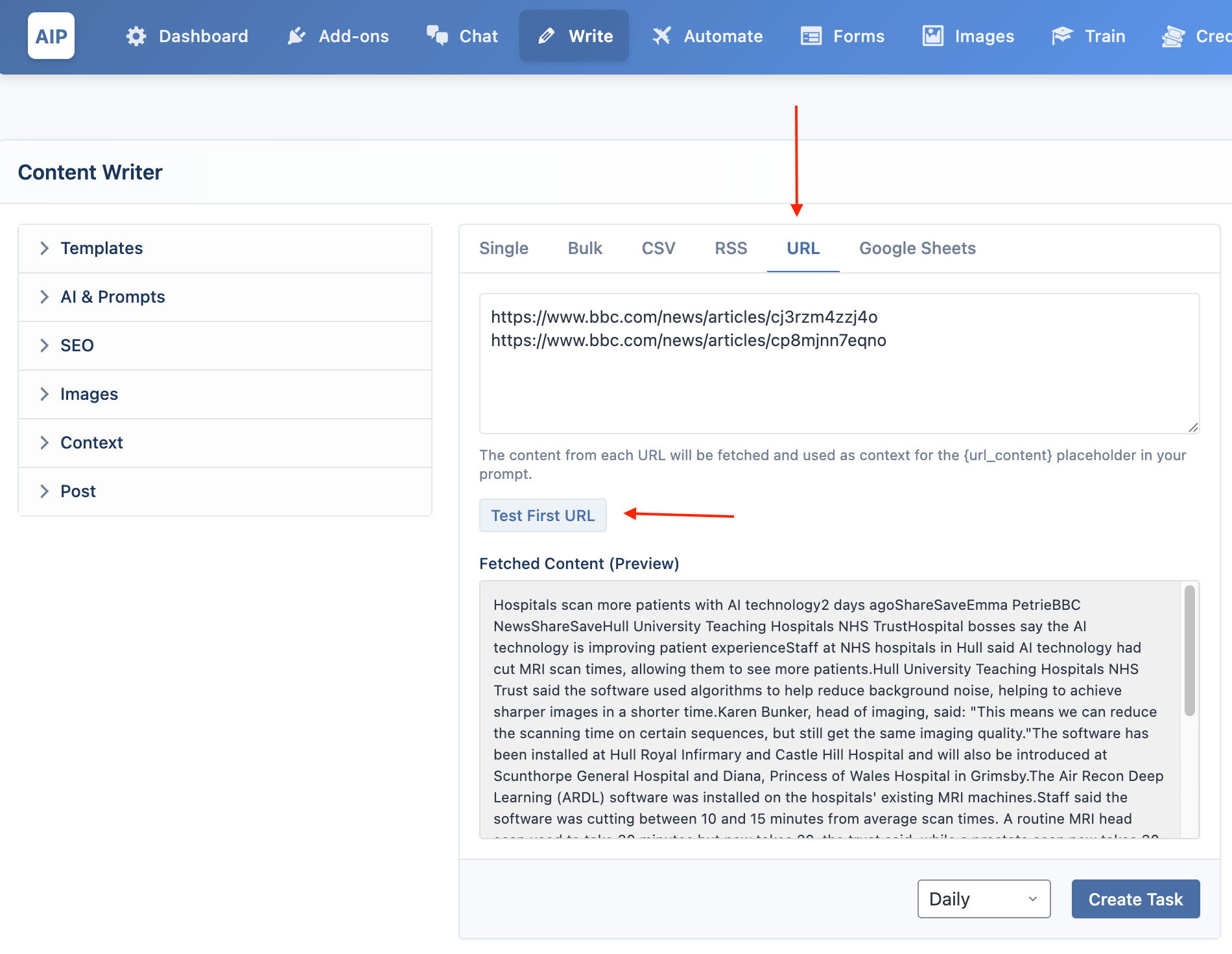
- Format: Enter one website URL per line.
- Prompting: The content from each URL will be fetched and made available in your prompt using the
{url_content}placeholder. - Testing: You can use the Test First URL button to preview the content that will be fetched from the first URL in your list.
Google Sheets
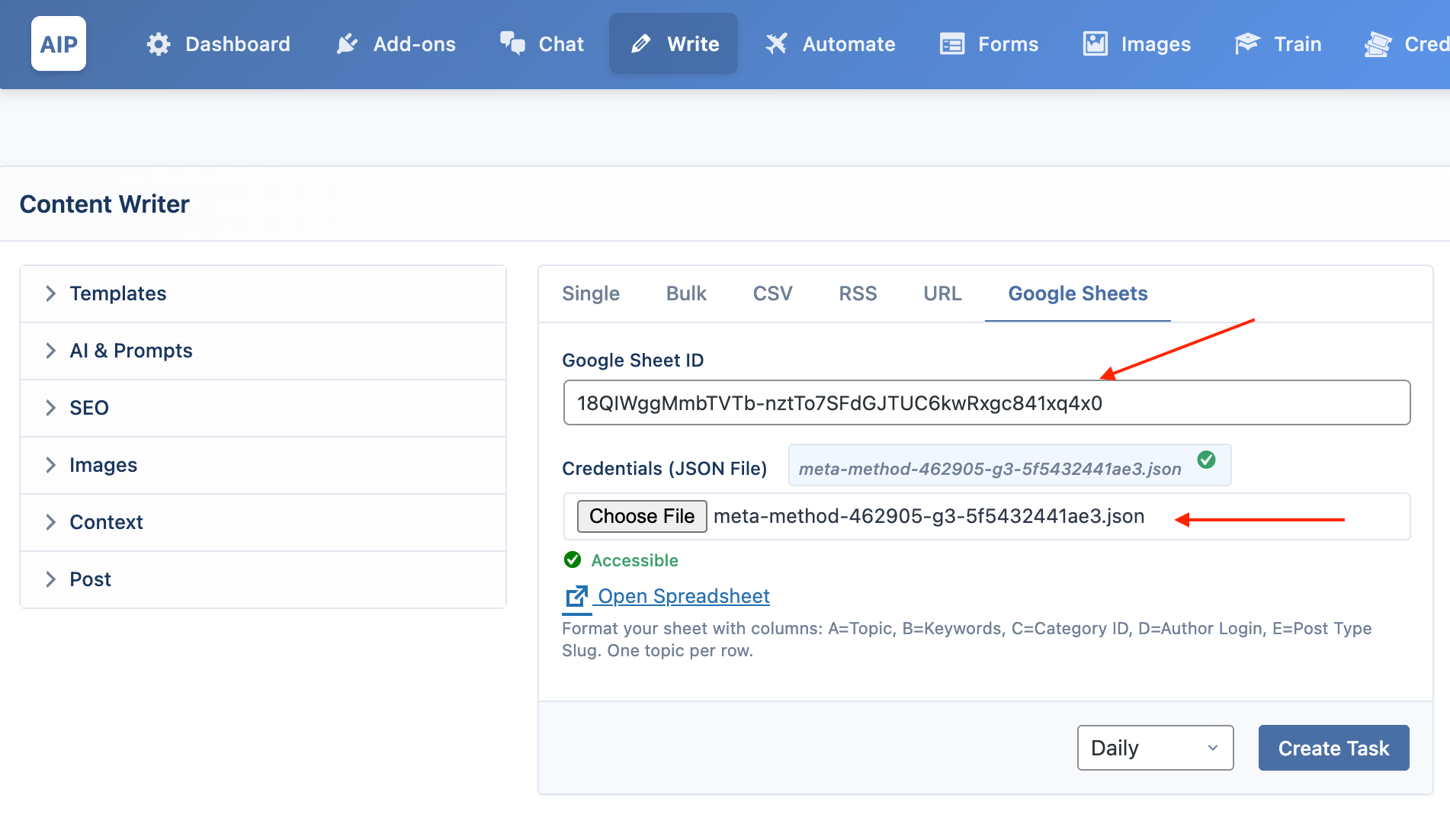
Connect a Google Sheet to manage a large content calendar. The task will generate articles from the topics listed in your sheet.
- Format: Your sheet must have columns in the following order:
- Column A: Topic
- Column B: Keywords
- Column C: Category ID
- Column D: Author Username
- Column E: Post Type Slug
- Column F: Schedule Date (YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM)
- Column G: Status (Optional). The plugin will write "Processed on [Date]" to this column after successfully generating an article. Rows with any value in the Status column will be skipped in future runs.
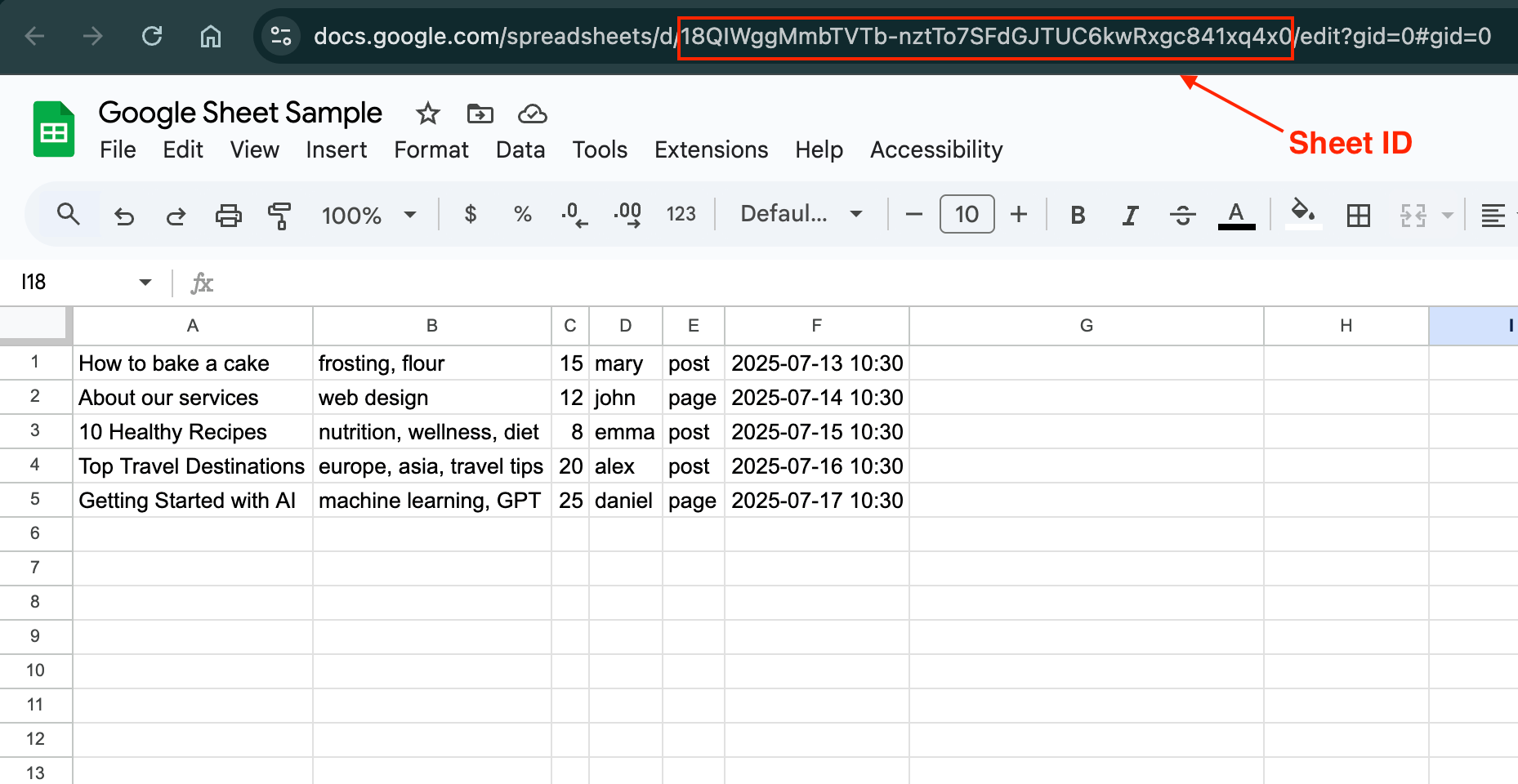
- Authentication: You will need to provide your Google Sheet ID and Service Account credentials. Ensure you have shared your Google Sheet with the
client_emailfound in your credentials file.
Creating Google Service Account
To use the Google Sheets feature, create a service account in your Google Cloud Console and upload your credentials to the plugin.
Follow these steps:
-
Visit your Google Cloud Console dashboard.
-
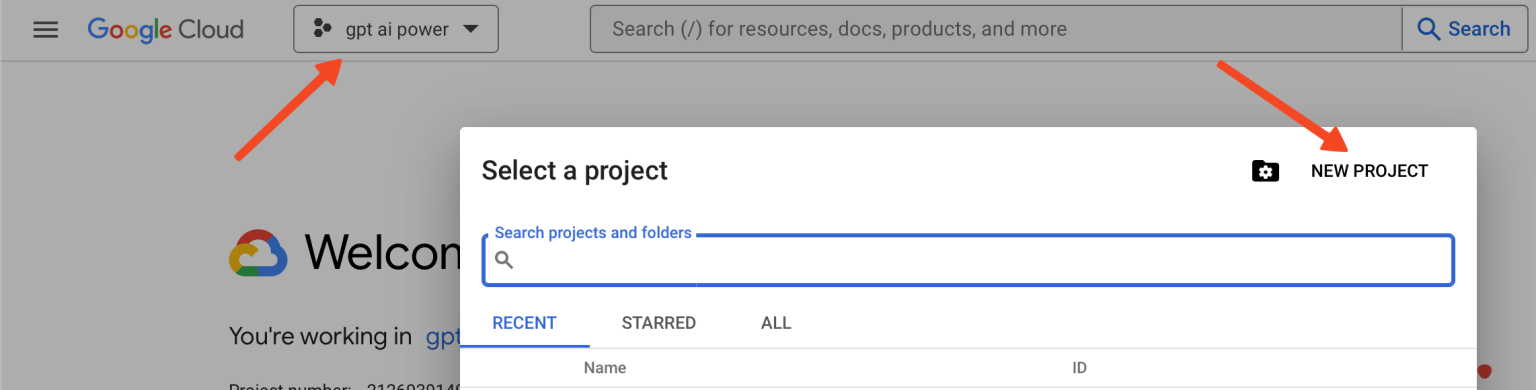
Click the dropdown menu in the top left corner and select Create new project.
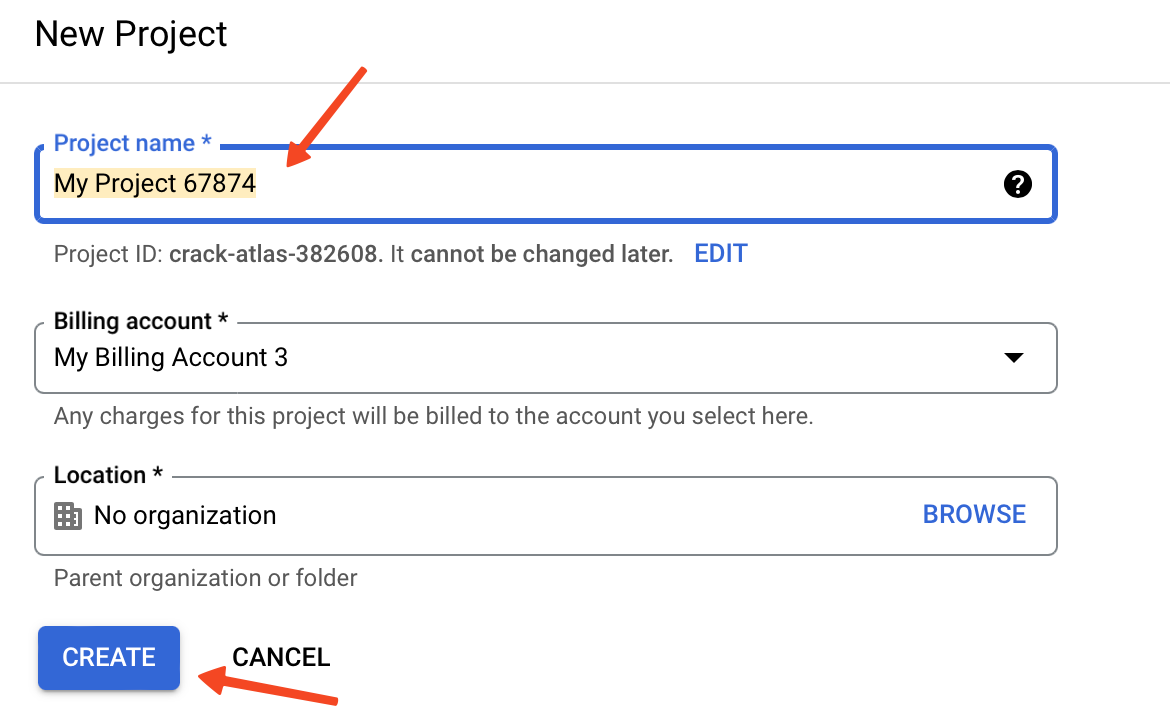
- Name your project or use the default name, then click Create.
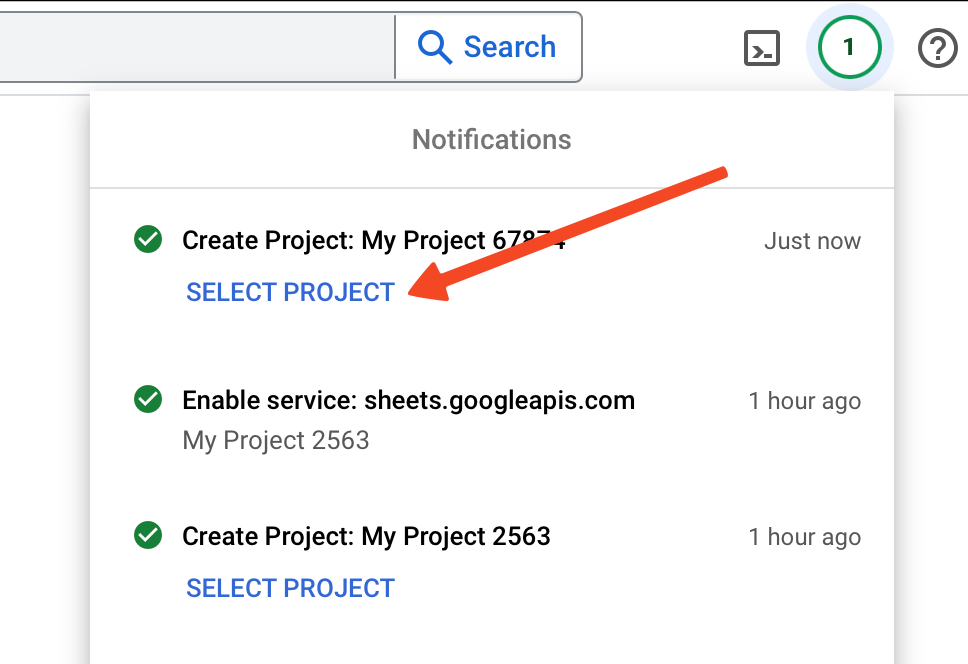
- Select your project.
- Click on the Dashboard link.
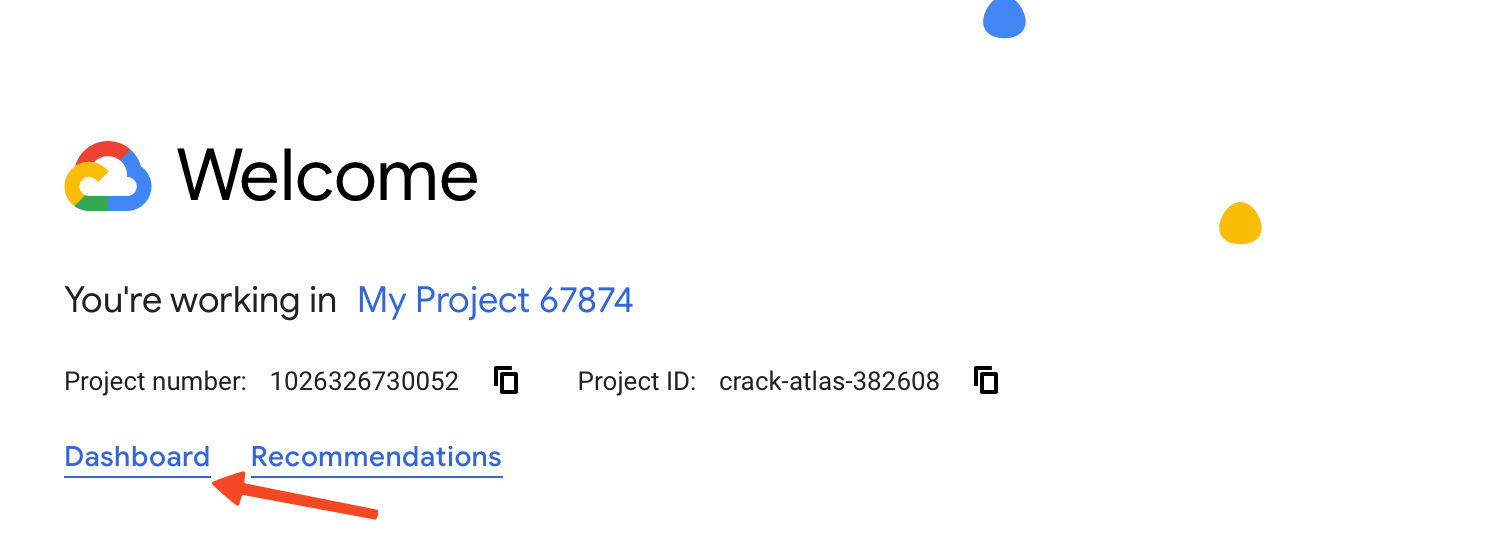
- Click on Go to APIs Overview.
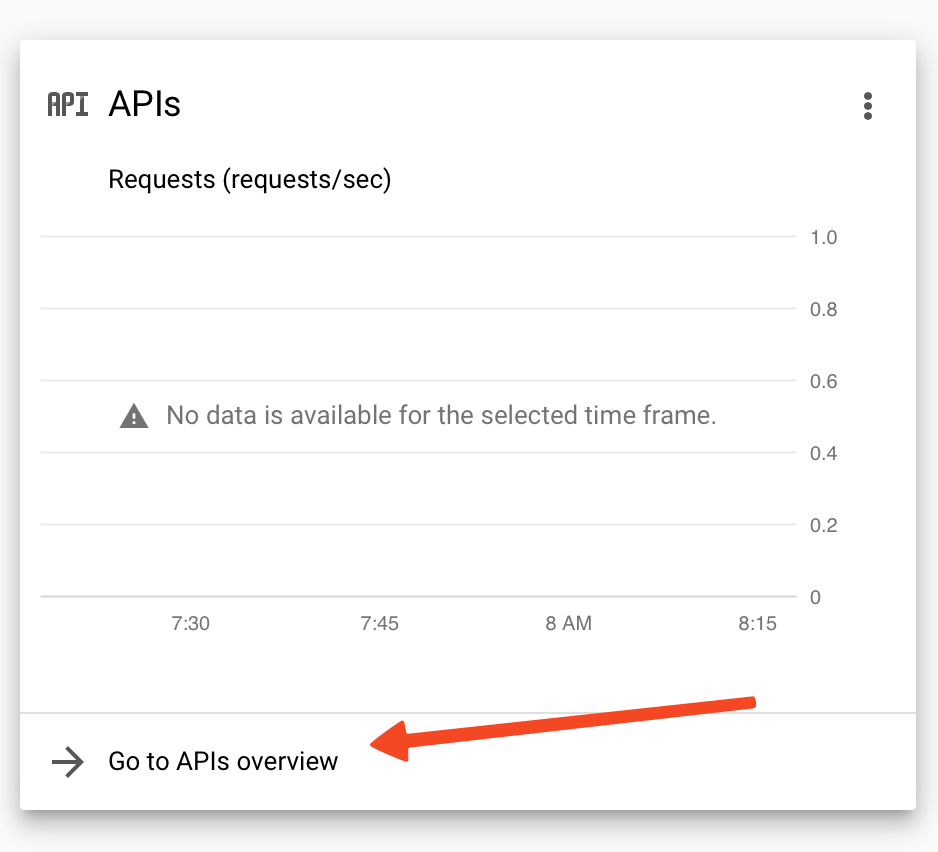
- Click on Enable APIs and Services.
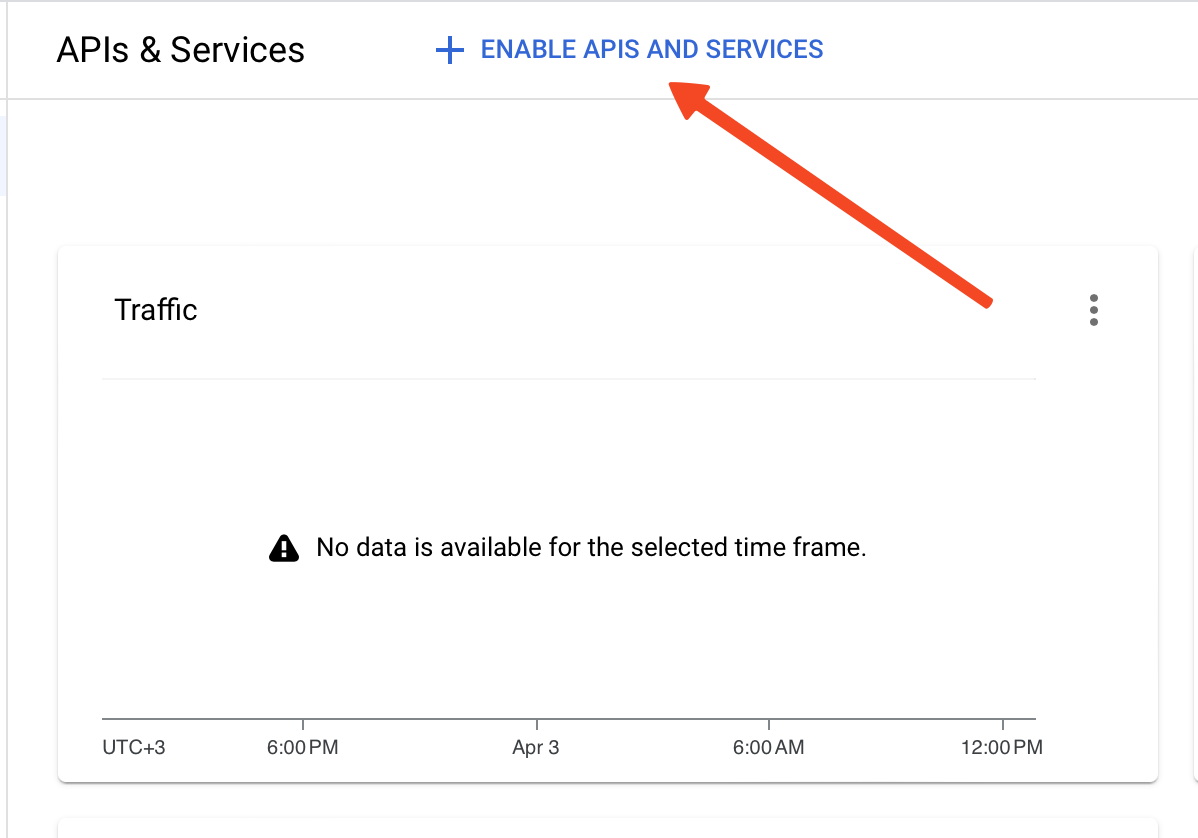
- Type Sheet and press enter.
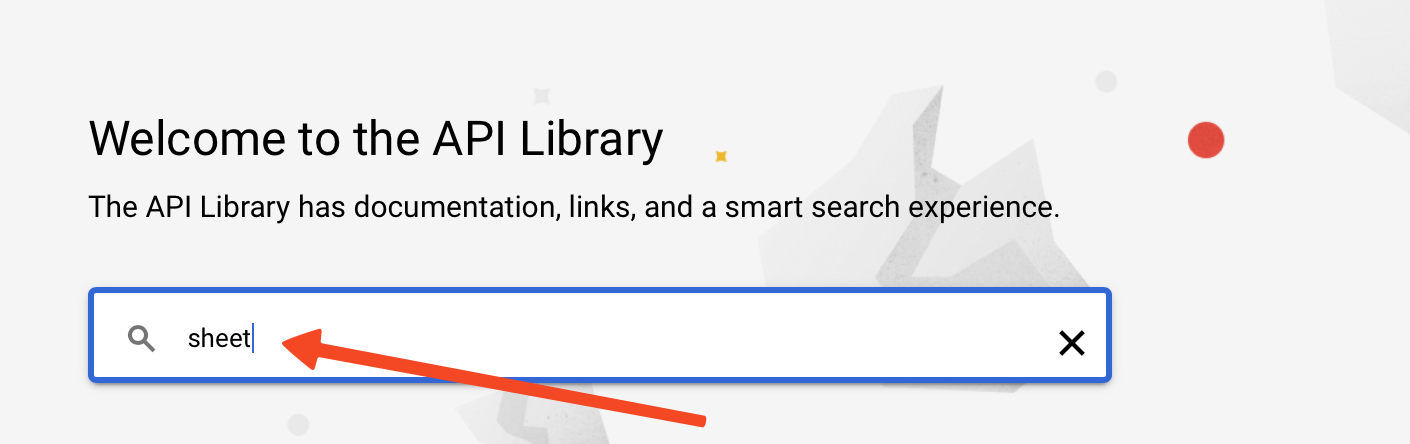
- Click on Google Sheets API.
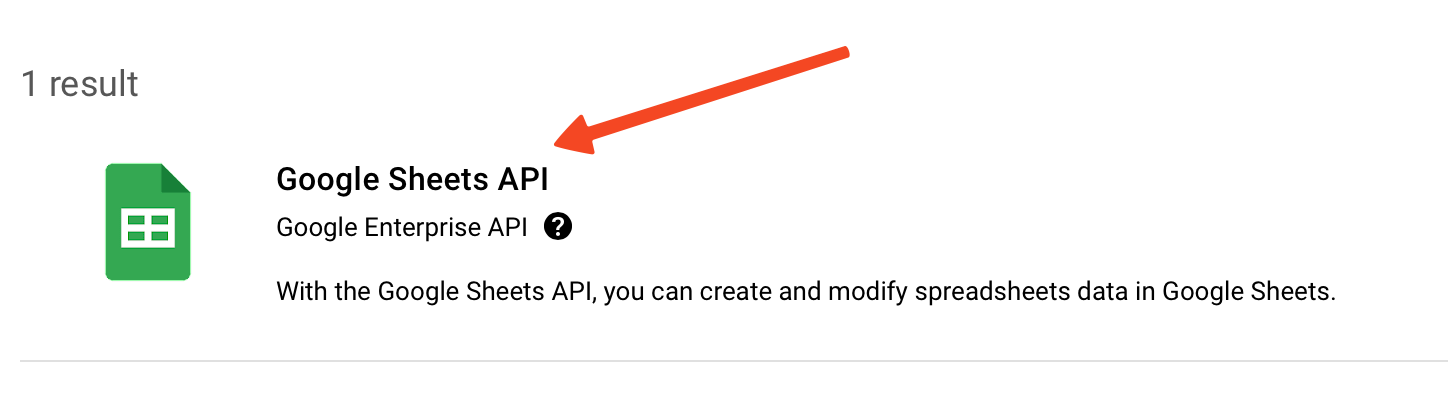
- Click the Enable button.

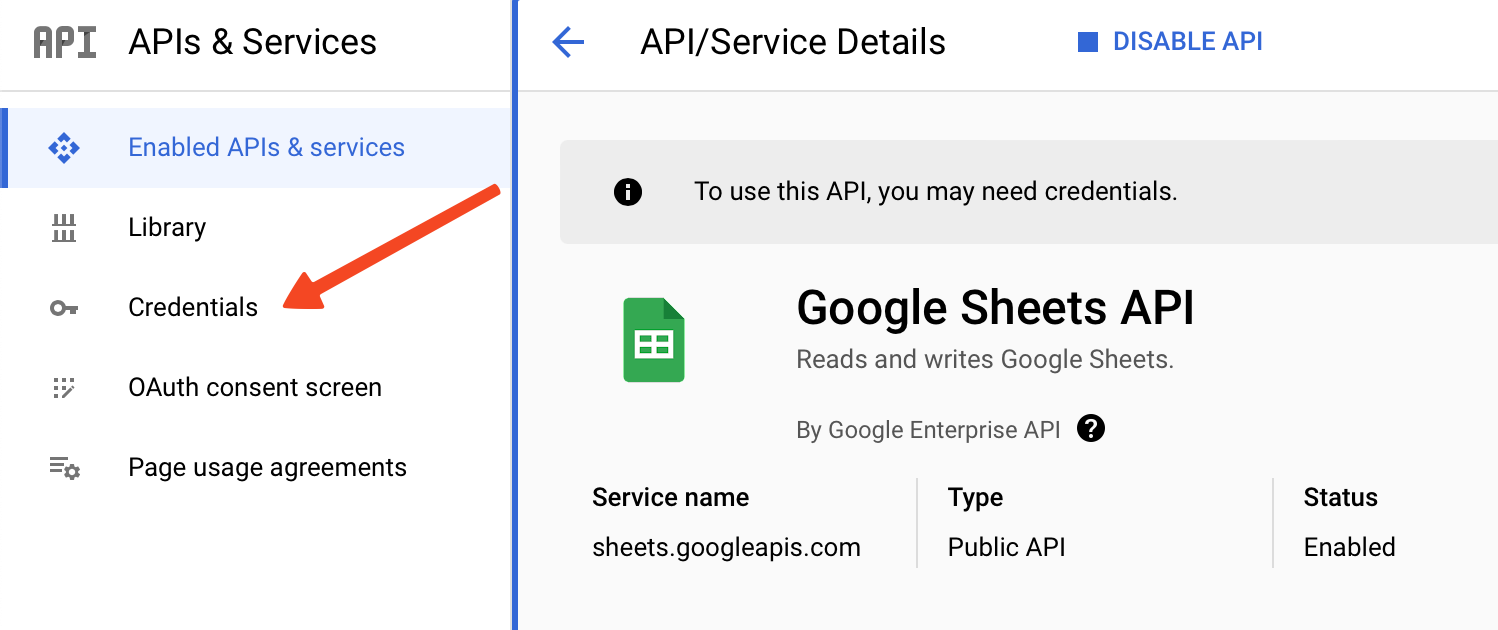
- Navigate to Credentials.
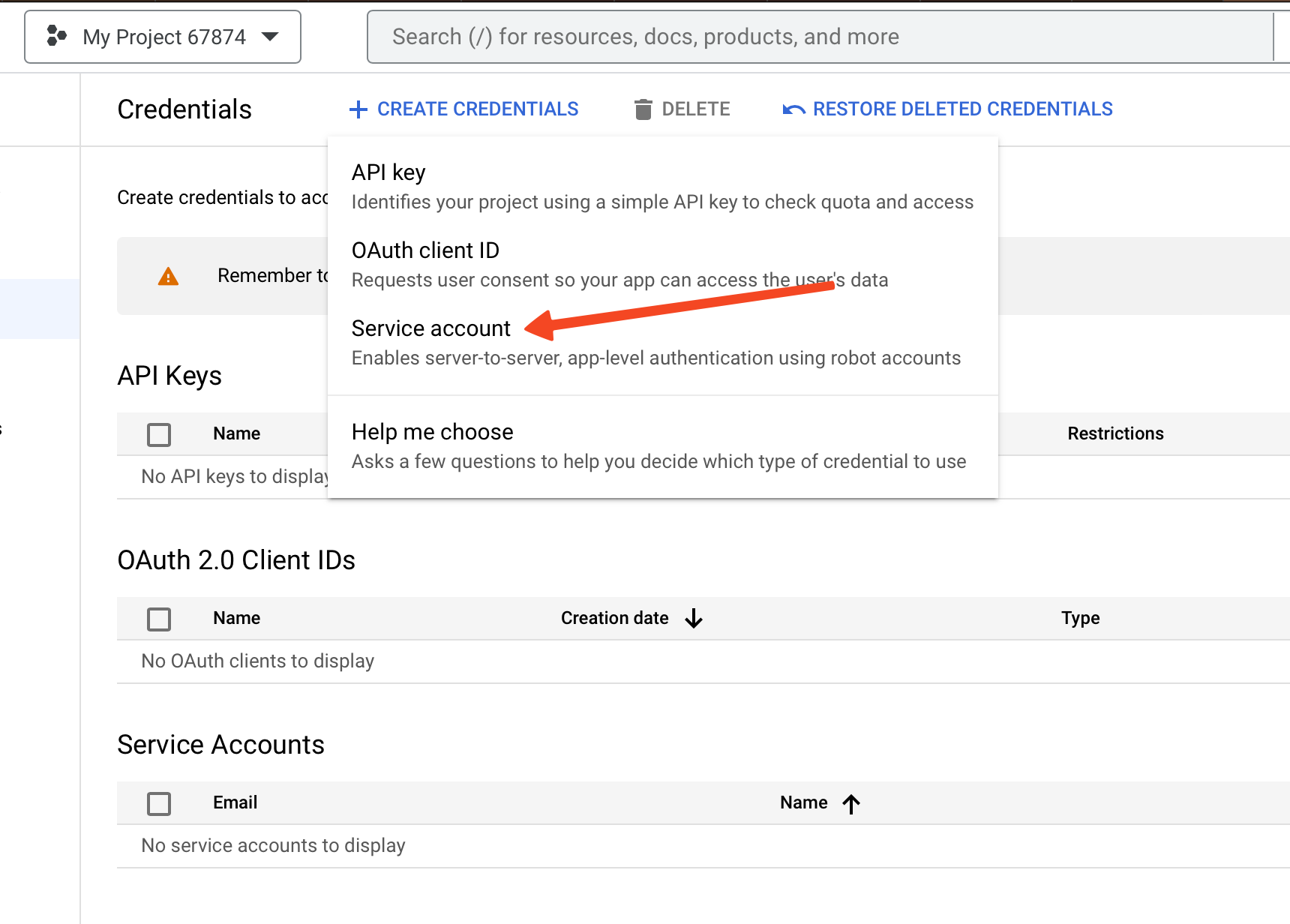
- Click on Create credentials and choose Service Account.
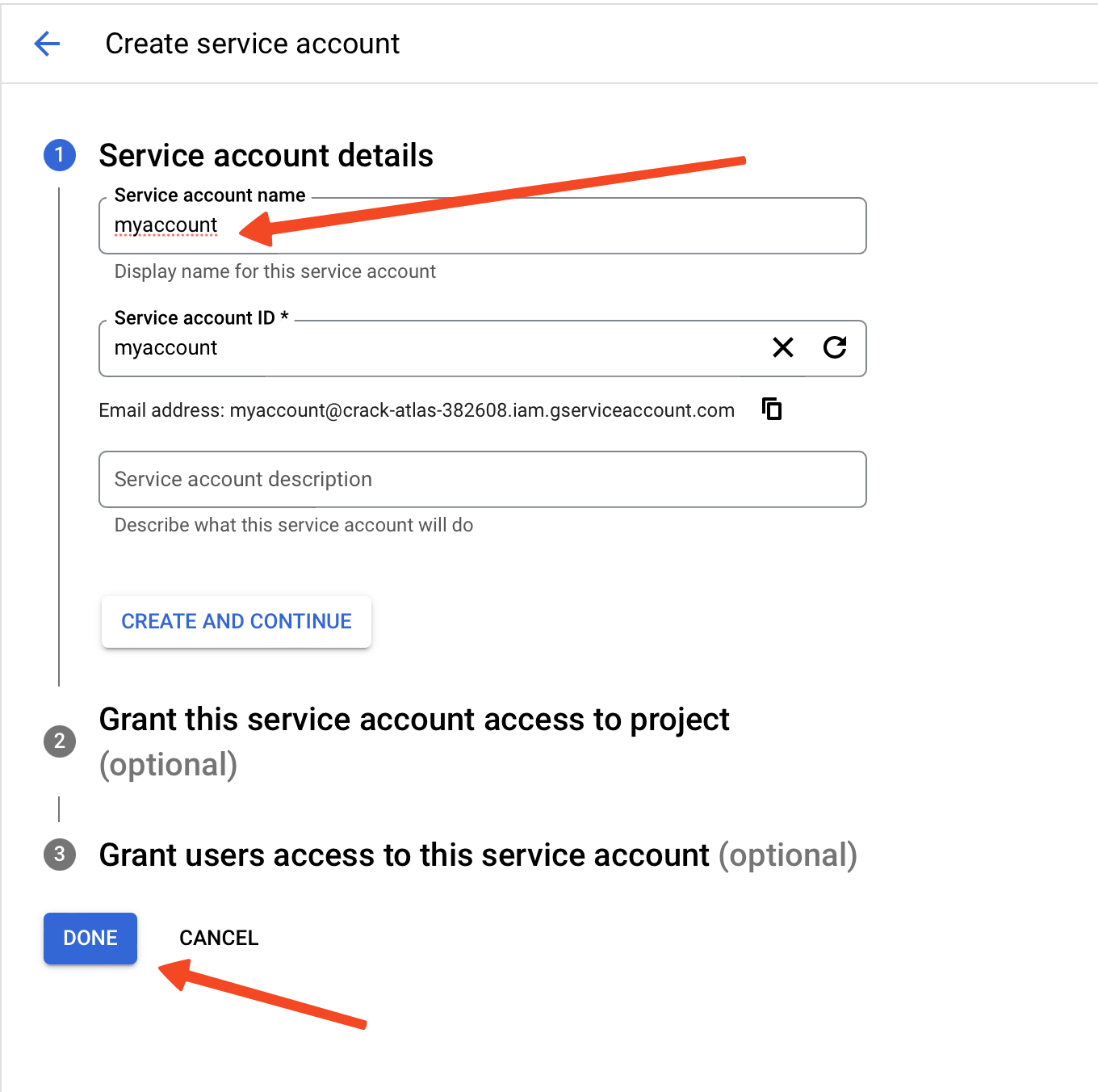
- Assign a name to your service account and click the Done button at the bottom.
- Click on your service account.
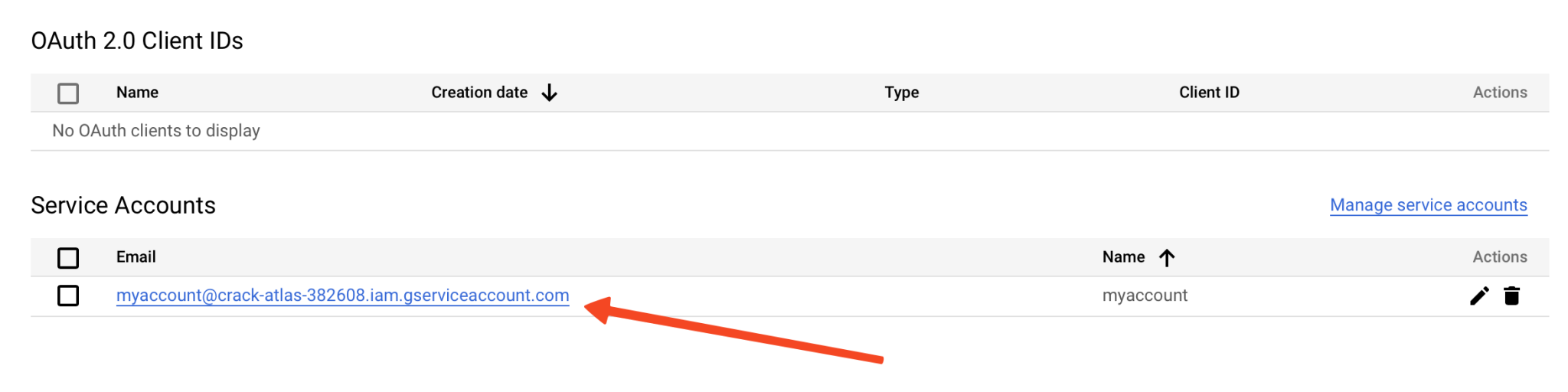
- Go to the Keys tab.
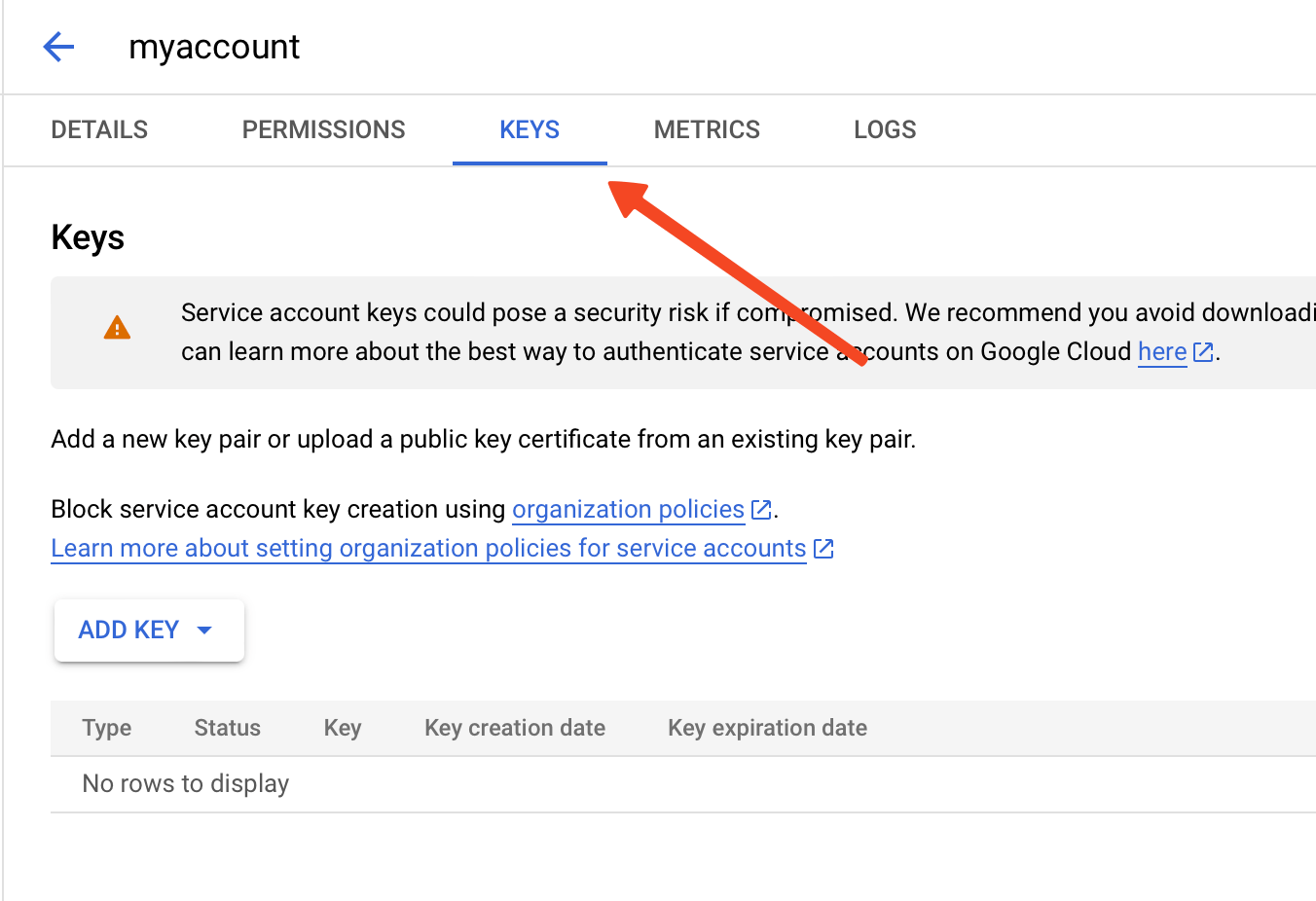
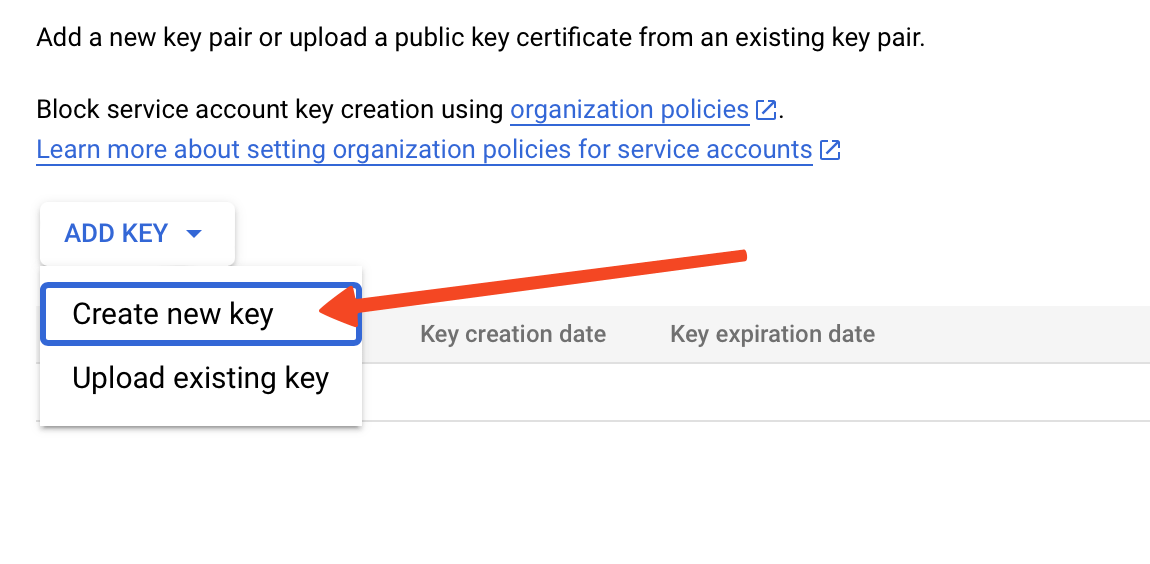
- Click on Add Key and select Create new key.
- Choose JSON and click Create.
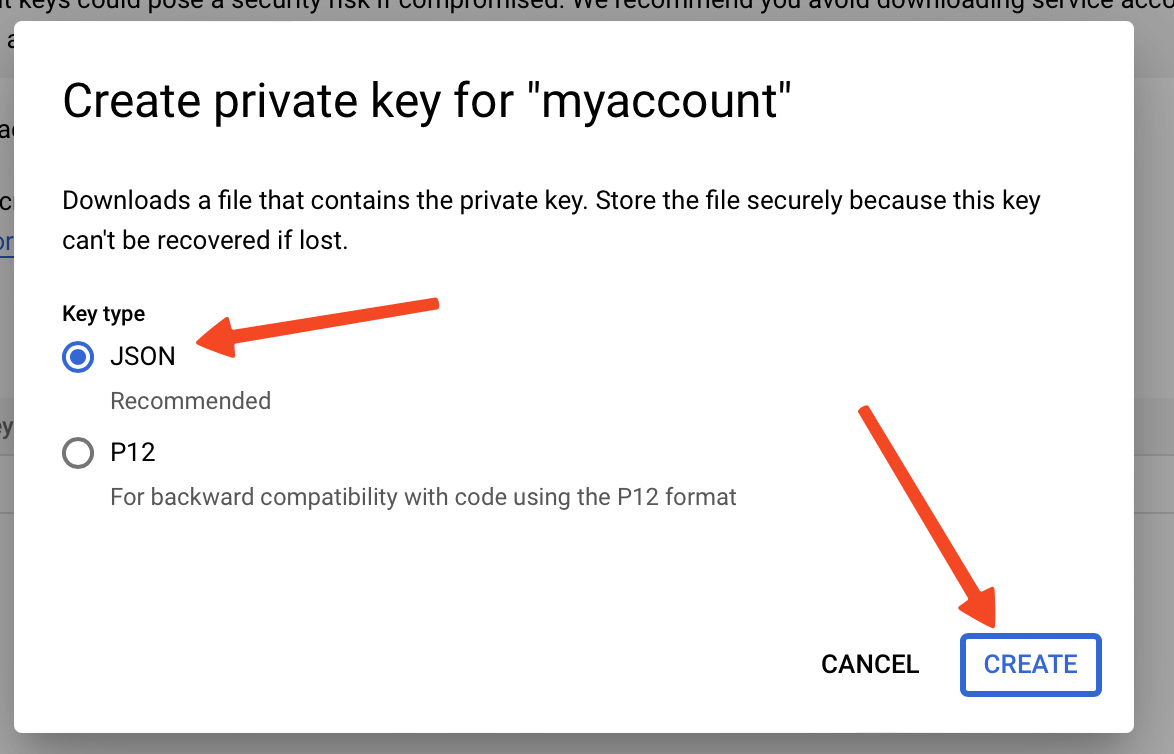
- This action will save your private key to your computer, likely in the Downloads folder.
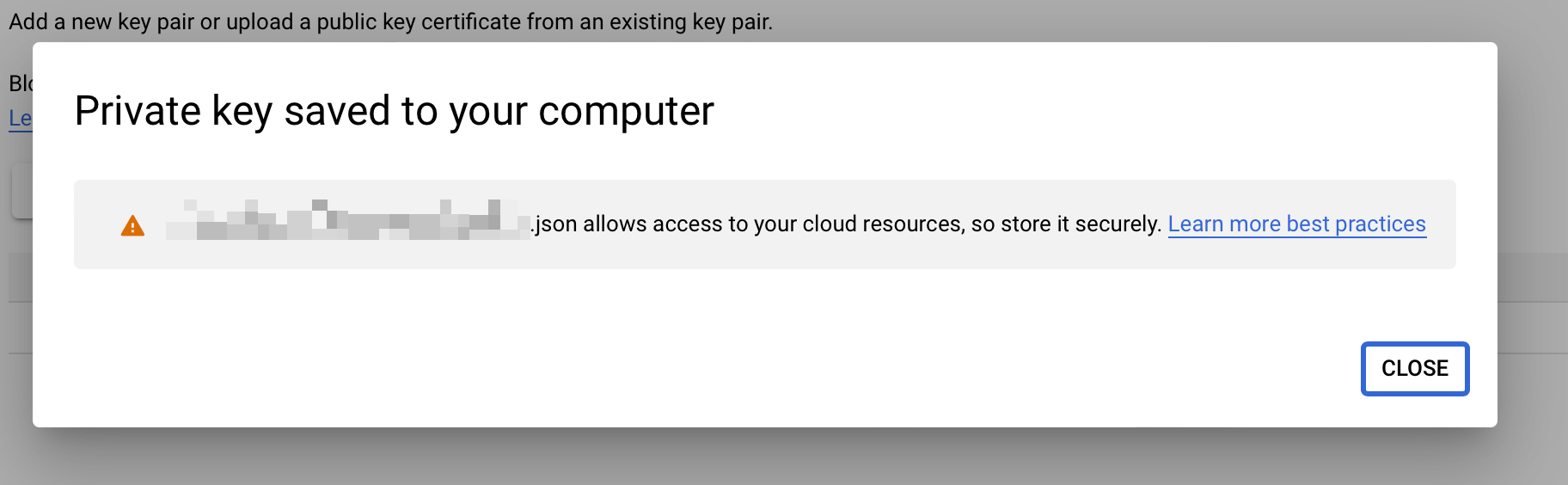
- Locate the downloaded credentials file (JSON) in your download folder; this file grants access to the Google Sheets API.
- In the plugin's “Write” page, go to the Google Sheets tab and click Choose to upload your JSON file. Make sure to enter your Google Sheet ID too.

-
Click the Create Task button.
-
A success message should appear, indicating that the file has been successfully uploaded.
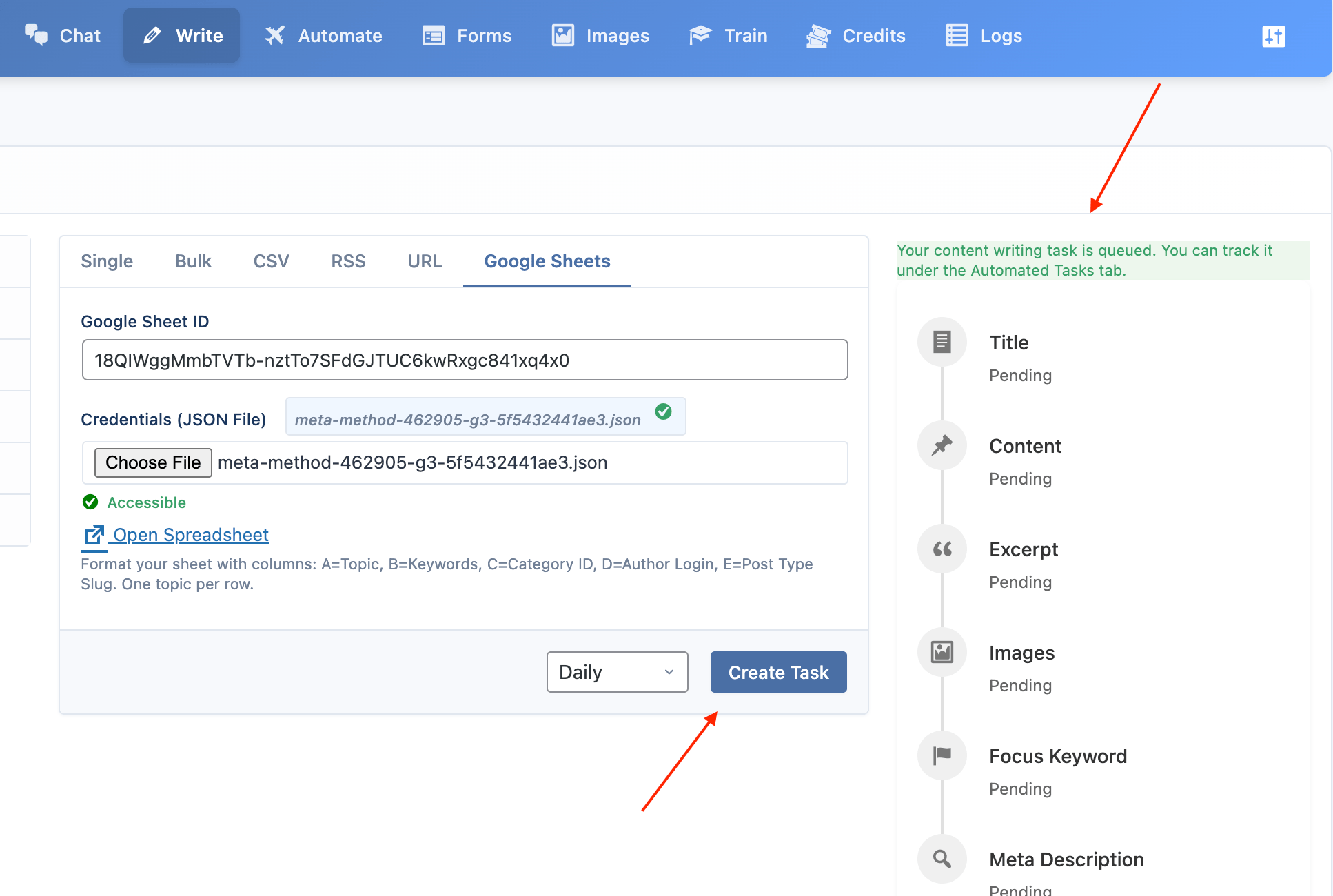
Congratulations! You’ve successfully created and uploaded your credentials.
Setting Up Google Sheets
It's time to create a Google Sheet, grant write permissions to the service account we just set up, and enter the Google Sheet URL in the designated field.
- Visit your Google Drive.
- Create a new folder.
- Download the sample file found under the Google Sheets tab or you can download it from here.
- Upload the sample file to your folder.

-
Open the sample file by double-clicking on it.
-
Click the Share button in the top right corner.
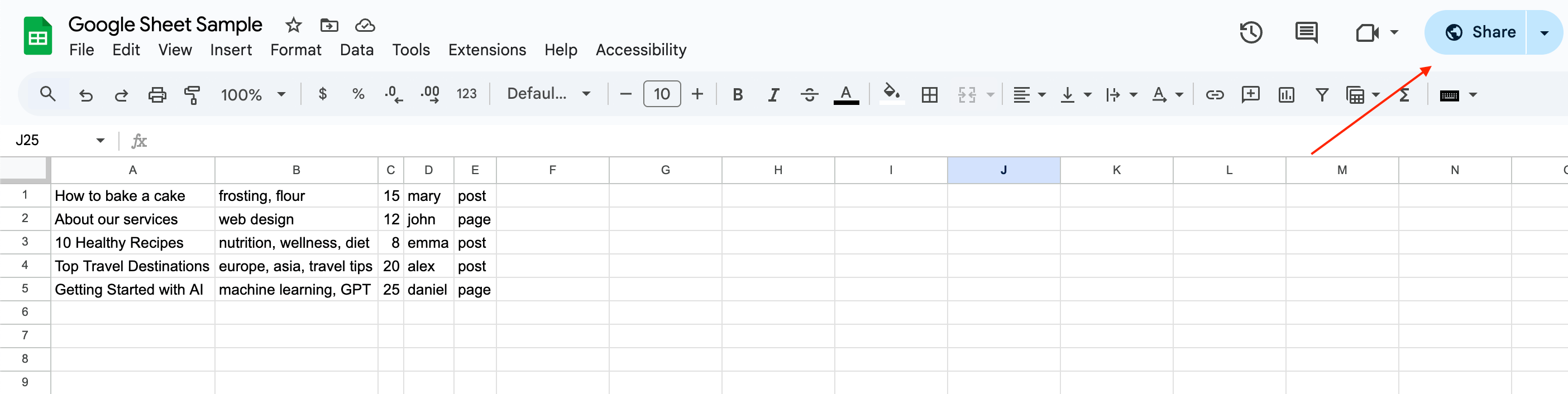
- Return to your Google Console and copy the service account address.
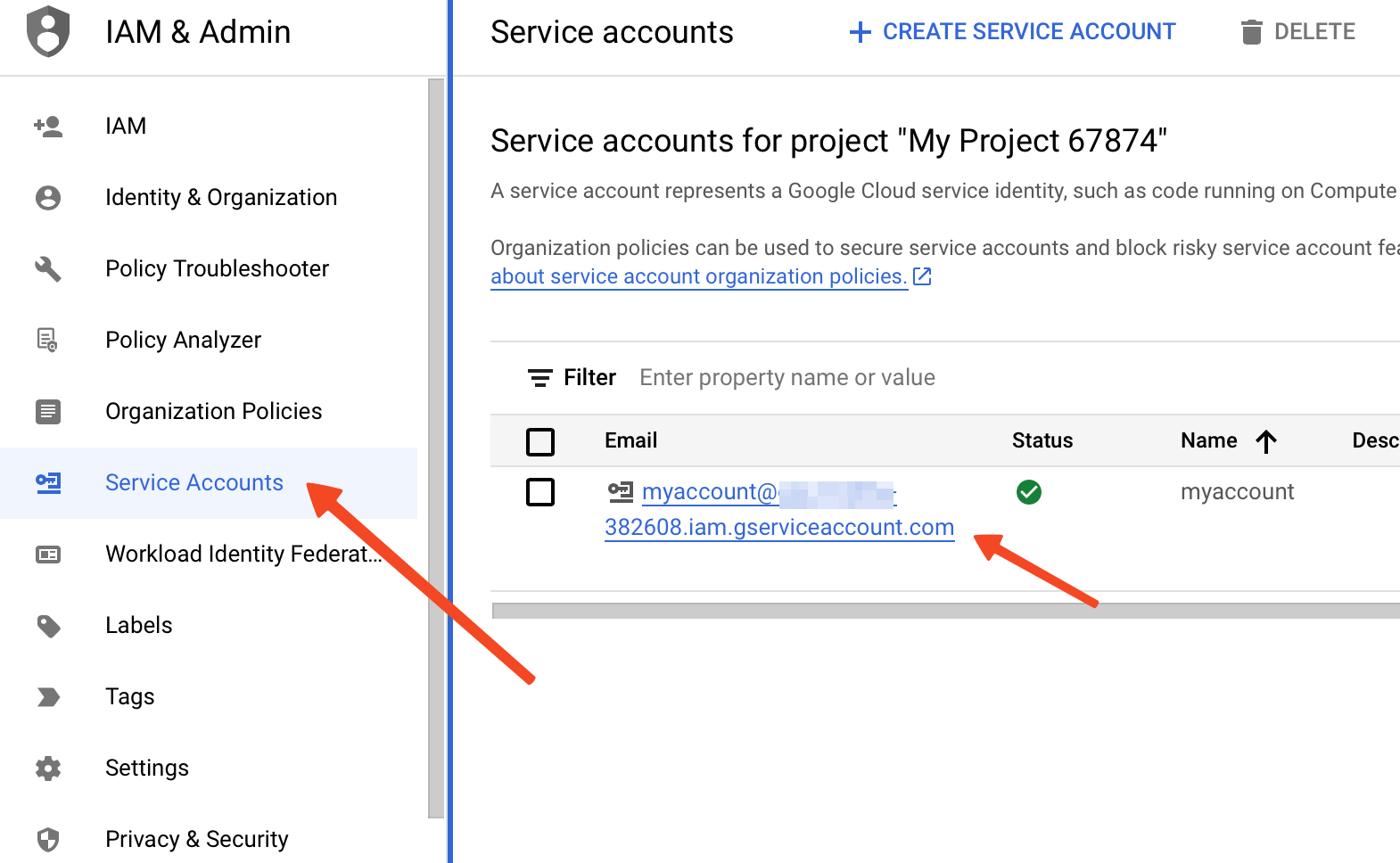
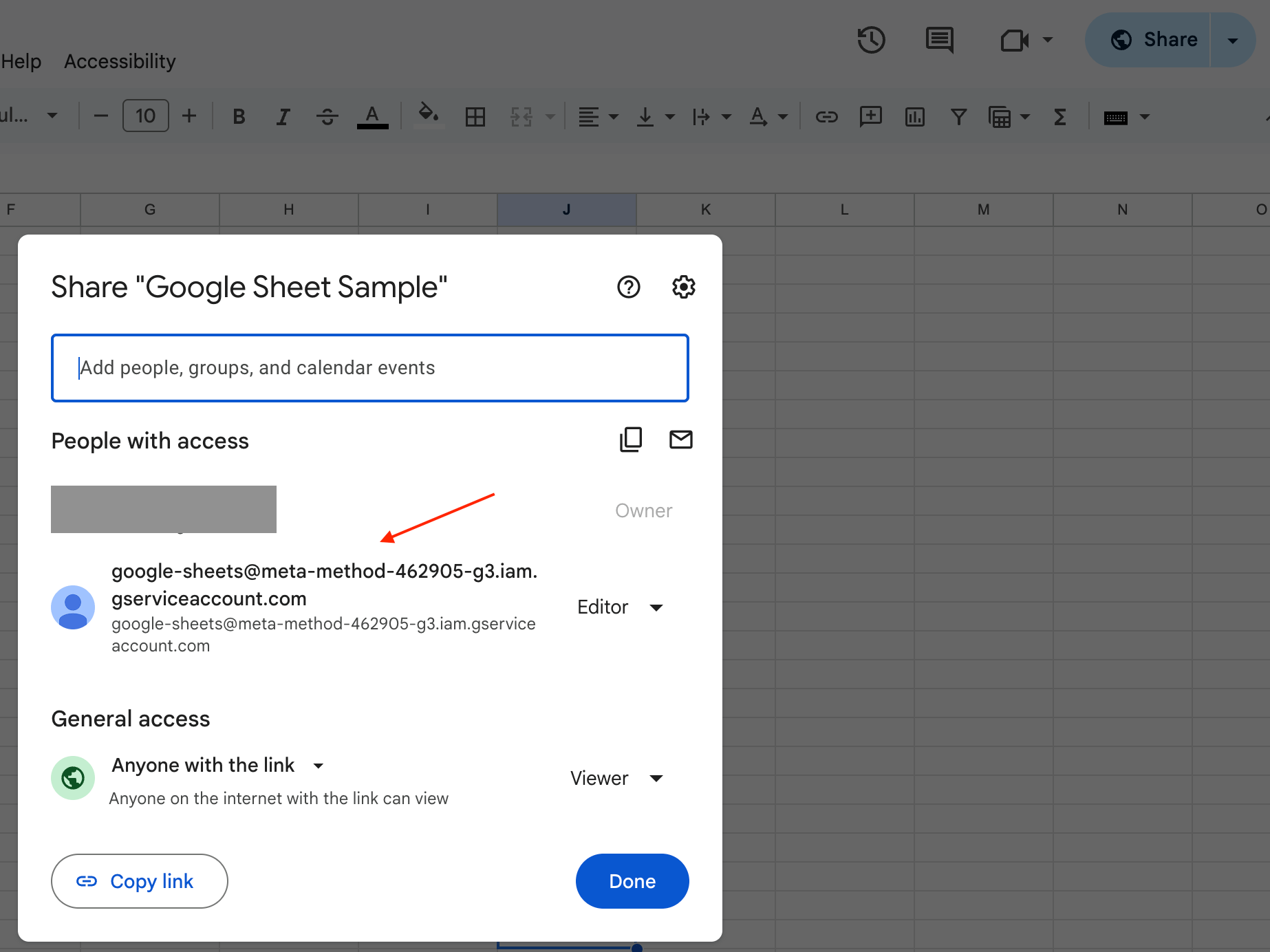
- Go back to Google Sheets and add this address in the share window. Ensure you select Editor and click the Share button.
-
This action shares your Google Sheet with your service account, allowing it to update the sheet.
-
You can now enter your titles, keywords, and other details per row.
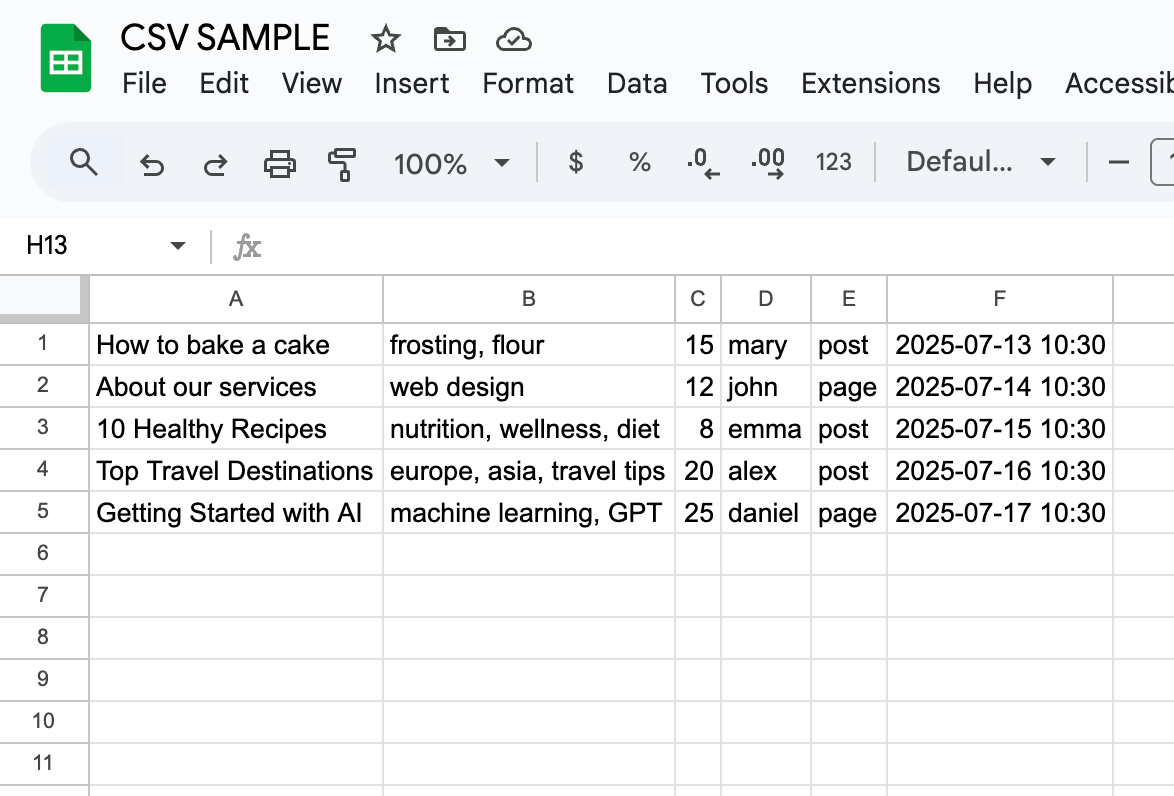
Column Definitions
| Column | Field Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| A | Topic | Mandatory. The main subject of the article. |
| B | Keywords | Optional. Comma-separated keywords to guide the AI. |
| C | Category ID | Optional. WordPress numeric category ID. |
| D | Author Login | Optional. WordPress username of the author. |
| E | Post Type Slug | Optional. Slug for post type (e.g., post, page). |
| F | Schedule Date | Optional. YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM format. |
| G | Status | Optional. The plugin writes "Processed" here and skips rows with a value in this column. |
One topic per row is required.